| Name | mult() |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examples |
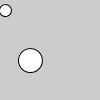
v = PVector(5, 10, 0) ellipse(v.x, v.y, 12, 12) v.mult(6) ellipse(v.x, v.y, 24, 24) 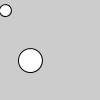
v1 = PVector(5, 10, 0) ellipse(v1.x, v1.y, 12, 12) v2 = PVector.mult(v1, 6) ellipse(v2.x, v2.y, 24, 24) | ||||||
| Description | Multiplies a vector by a scalar. The version of the method that uses a float acts directly on the vector upon which it is called (as in the first example above), and therefore has no return value. The versions that receive both a PVector and a float as arugments are static methods, and each returns a new PVector that is the result of the multiplication operation. Both examples above produce the same visual output. | ||||||
| Syntax | .mult(n) .mult(v, n) .mult(v, n, target) | ||||||
| Parameters |
|
Updated on Tue Feb 27 14:07:12 2024.
If you see any errors or have comments, please let us know.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License