| Name | PVector |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examples |
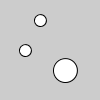
v1 = PVector(40, 20) v2 = PVector(25, 50) ellipse(v1.x, v1.y, 12, 12) ellipse(v2.x, v2.y, 12, 12) v2.add(v1) # v2 += v1 ellipse(v2.x, v2.y, 24, 24) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
A class to describe a two or three dimensional vector, specifically a Euclidean (also known as geometric) vector. A vector is an entity that has both magnitude and direction. The datatype, however, stores the components of the vector (x,y for 2D, and x,y,z for 3D). The magnitude and direction can be accessed via the methods mag() and heading(). In many of the Processing examples, you will see PVector used to describe a position, velocity, or acceleration. For example, if you consider a rectangle moving across the screen, at any given instant it has a position (a vector that points from the origin to its location), a velocity (the rate at which the object's position changes per time unit, expressed as a vector), and acceleration (the rate at which the object's velocity changes per time unit, expressed as a vector). Since vectors represent groupings of values, we'll need to do some "vector" math, which is made easy by the methods inside the PVector class, or, in Python Mode, in some cases the traditional mathematical operators have been "overloaded" to work with PVectors: "+" adds vectors, "-" subtracts vectors, "*" does scalar multiplication, and "/" does scalar division. The related augmented assigment operators, "+=", "-=", "*=", and "/=", also work. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Syntax | v = PVector(x, y) v = PVector(x, y, z) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameters |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methods |
|
Updated on Tue Feb 27 14:07:12 2024.
If you see any errors or have comments, please let us know.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License